Tune in to video discussions about XGEVA® in clinical trials
Hear how Dr. Henry uses XGEVA® with his Metastatic Breast and Prostate cancer Patients
Video Length [11:37]
Hear how Dr. Henry uses XGEVA® with his Metastatic Breast and Prostate cancer Patients
Video Length [15:01]
Hear how Dr. Henry uses XGEVA® with his Metastatic Breast and Prostate cancer Patients
Video Length [14:24]
Hear how Dr. Henry uses XGEVA® with his Metastatic Breast and Prostate cancer Patients
Video Length [15:50]



Hear how Dr. Berenson uses XGEVA® with his Multiple Myeloma Patients
Video Length [04:47]
Hear how Dr. Berenson uses XGEVA® with his Multiple Myeloma Patients
Video Length [10:46]
Hear how Dr. Berenson uses XGEVA® with his Multiple Myeloma Patients
Video Length [09:48]



A panel discussion with Dr. Francis Arena and Dr. Noam Drazin
Video Length [15:41]
A panel discussion with Dr. Francis Arena and Dr. Noam Drazin
Video Length [21:10]
A panel discussion with Dr. Francis Arena and Dr. Noam Drazin
Video Length [25:47]



A panel discussion with Dr. Neal Shore and Dr. Jorge Garcia
Video Length [11:23]
A panel discussion with Dr. Neal Shore and Dr. Jorge Garcia
Video Length [11:18]
A panel discussion with Dr. Neal Shore and Dr. Jorge Garcia
Video Length [25:23]


Watch as physicians identify appropriate patients for XGEVA®
No prior bone complication • No existing bone pain
Video Length [15:01]
Suffered one prior bone complication • Experiencing bone pain
Video Length [16:37]
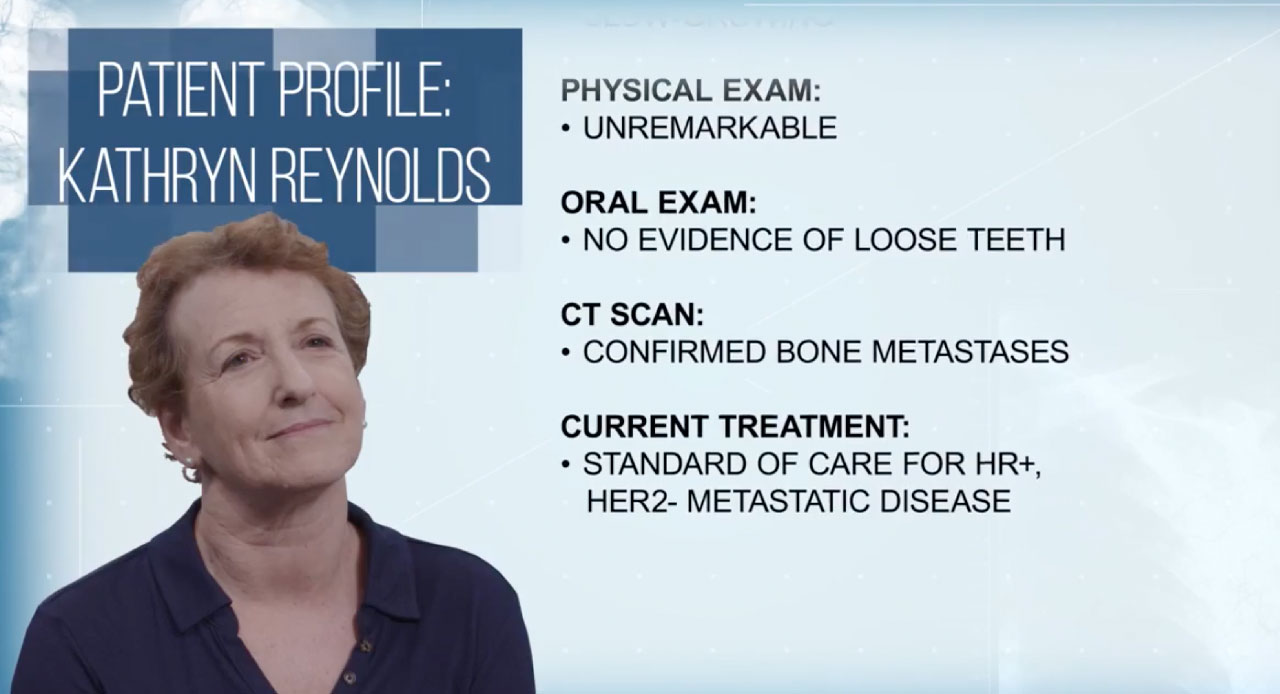
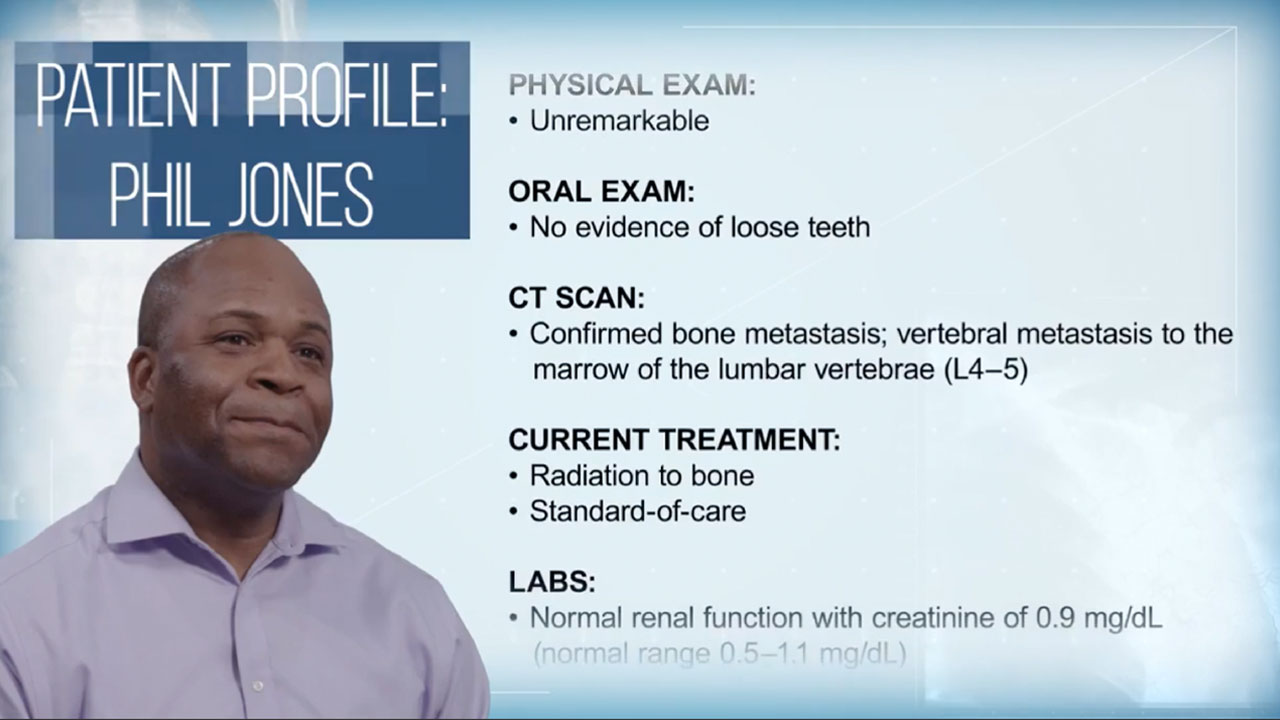
Hear three key members of a care team—a physician, an oncology nurse, and a patient—share their perspectives on XGEVA®
Video Length [10:03]
Video Length [9:44]
Video Length [8:36]



Meet three women with unique stories about living with bone metastases from breast cancer and receiving XGEVA®
Video Length [8:31]
Video Length [9:19]
Video Length [8:20]



Watch how multiple myeloma and bone metastases from solid tumors weaken bones
Video Length [1:46]
Video Length [2:45]
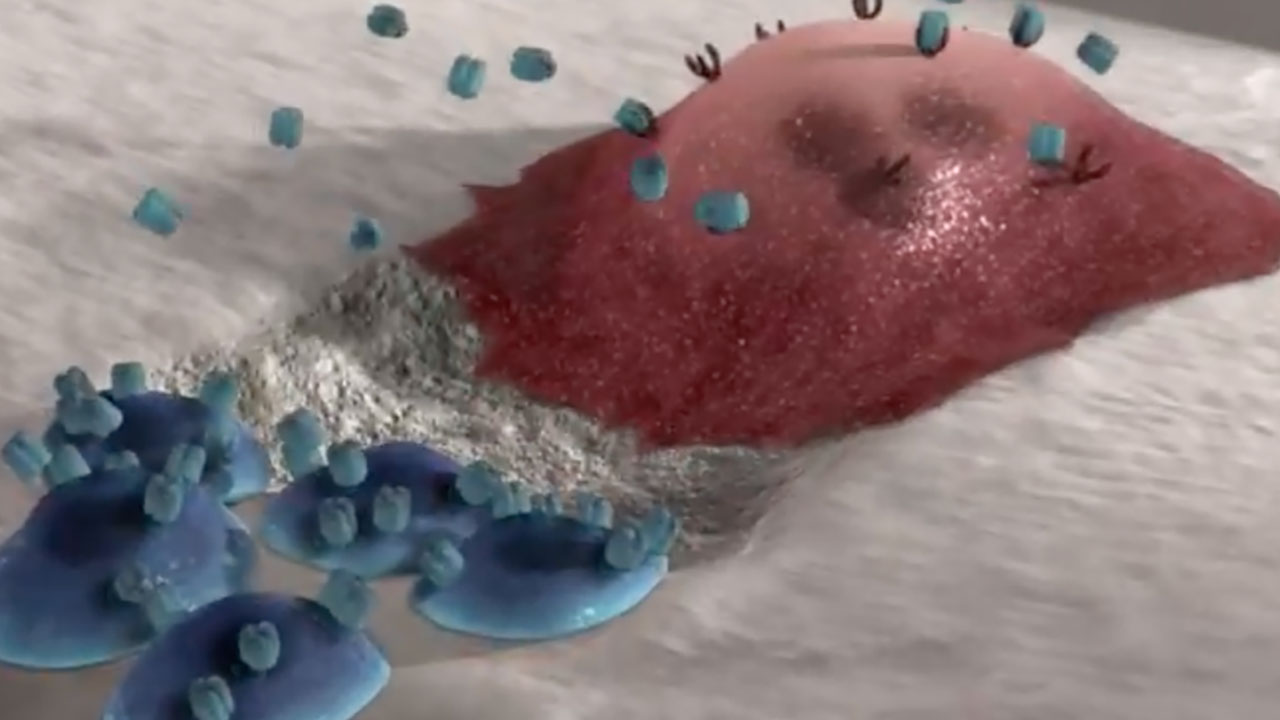

Mechanism of Disease (MOD)
See how XGEVA® blocks the function of RANK ligand (RANKL)
Video Length [1:31]
Video Length [1:56]
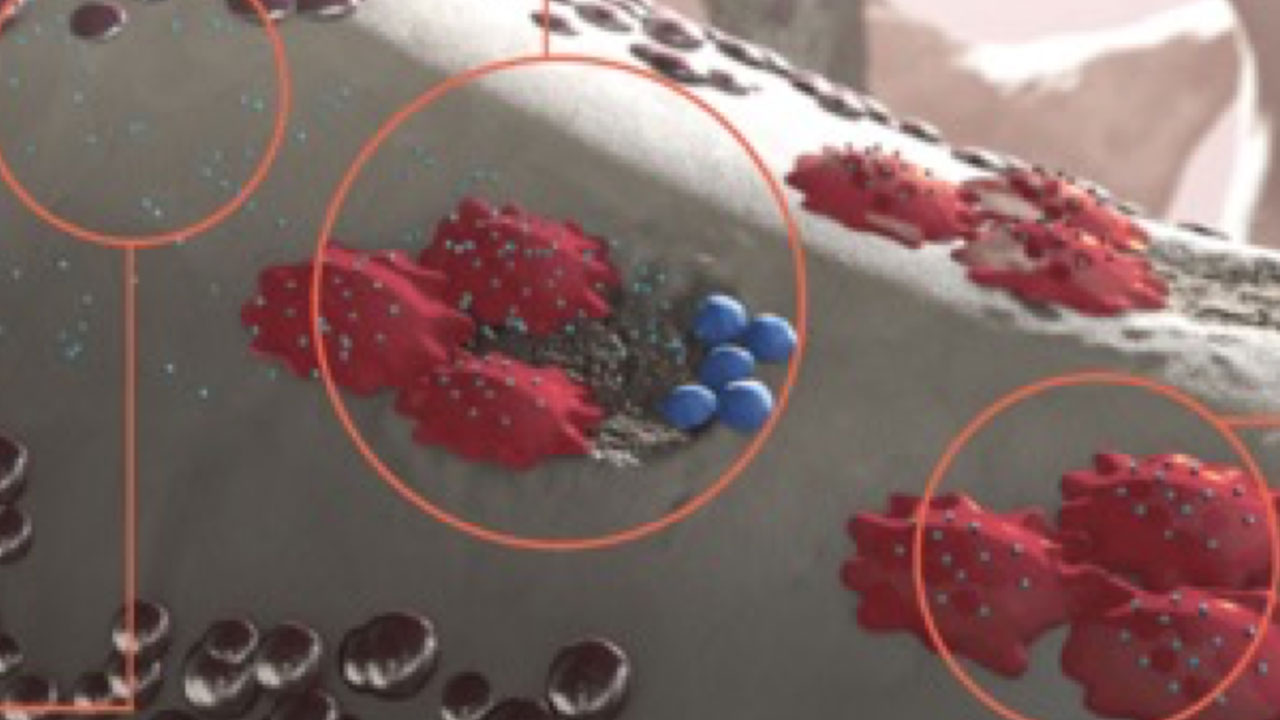
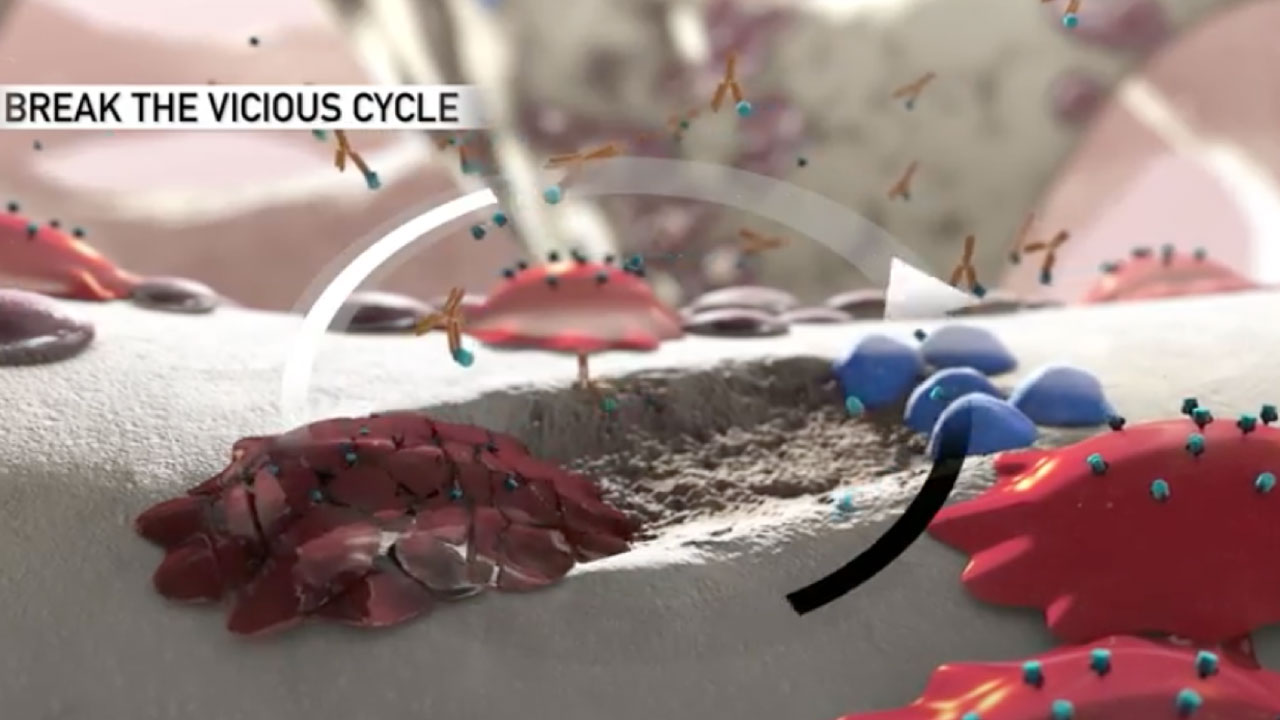
Mechanism of Action (MOA)
Three patients tell their stories about their passions, diagnoses and why they chose XGEVA®.
Breast Cancer
Video Length [3:38]
Prostate Cancer
Video Length [3:39]
Multiple Myeloma
Video Length [3:40]



Pre-existing hypocalcemia must be corrected prior to initiating therapy with XGEVA®. XGEVA® can cause severe symptomatic hypocalcemia, and fatal cases have been reported. Monitor calcium levels, especially in the first weeks of initiating therapy, and administer calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D as necessary. Concomitant use of calcimimetics and other drugs that can lower calcium levels may worsen hypocalcemia risk and serum calcium should be closely monitored. Advise patients to contact a healthcare professional for symptoms of hypocalcemia.
An increased risk of hypocalcemia has been observed in clinical trials of patients with increasing renal dysfunction, most commonly with severe dysfunction (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/minute and/or on dialysis), and with inadequate/no calcium supplementation. Monitor calcium levels and calcium and vitamin D intake.
XGEVA® is contraindicated in patients with known clinically significant hypersensitivity to XGEVA®, including anaphylaxis that has been reported with use of XGEVA®. Reactions may include hypotension, dyspnea, upper airway edema, lip swelling, rash, pruritus, and urticaria. If an anaphylactic or other clinically significant allergic reaction occurs, initiate appropriate therapy and discontinue XGEVA® therapy permanently.
Patients receiving XGEVA® should not take Prolia® (denosumab).
Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) has been reported in patients receiving XGEVA®, manifesting as jaw pain, osteomyelitis, osteitis, bone erosion, tooth or periodontal infection, toothache, gingival ulceration, or gingival erosion. Persistent pain or slow healing of the mouth or jaw after dental surgery may also be manifestations of ONJ. In clinical trials in patients with cancer, the incidence of ONJ was higher with longer duration of exposure.
Patients with a history of tooth extraction, poor oral hygiene, or use of a dental appliance are at a greater risk to develop ONJ. Other risk factors for the development of ONJ include immunosuppressive therapy, treatment with angiogenesis inhibitors, systemic corticosteroids, diabetes, and gingival infections.
Perform an oral examination and appropriate preventive dentistry prior to the initiation of XGEVA® and periodically during XGEVA® therapy. Advise patients regarding oral hygiene practices. Avoid invasive dental procedures during treatment with XGEVA®. Consider temporarily interrupting XGEVA® therapy if an invasive dental procedure must be performed.
Patients who are suspected of having or who develop ONJ while on XGEVA® should receive care by a dentist or an oral surgeon. In these patients, extensive dental surgery to treat ONJ may exacerbate the condition.
Atypical femoral fracture has been reported with XGEVA®. These fractures can occur anywhere in the femoral shaft from just below the lesser trochanter to above the supracondylar flare and are transverse or short oblique in orientation without evidence of comminution.
Atypical femoral fractures most commonly occur with minimal or no trauma to the affected area. They may be bilateral and many patients report prodromal pain in the affected area, usually presenting as dull, aching thigh pain, weeks to months before a complete fracture occurs. A number of reports note that patients were also receiving treatment with glucocorticoids (e.g. prednisone) at the time of fracture. During XGEVA® treatment, patients should be advised to report new or unusual thigh, hip, or groin pain. Any patient who presents with thigh or groin pain should be suspected of having an atypical fracture and should be evaluated to rule out an incomplete femur fracture. Patients presenting with an atypical femur fracture should also be assessed for symptoms and signs of fracture in the contralateral limb. Interruption of XGEVA® therapy should be considered, pending a risk/benefit assessment, on an individual basis.
Clinically significant hypercalcemia requiring hospitalization and complicated by acute renal injury has been reported in XGEVA®-treated patients with GCTB and in patients with growing skeletons within one year of treatment discontinuation. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hypercalcemia after treatment discontinuation and treat appropriately.
Multiple vertebral fractures (MVF) have been reported following discontinuation of treatment with denosumab. Patients at higher risk for MVF include those with risk factors for or a history of osteoporosis or prior fractures. When XGEVA® treatment is discontinued, evaluate the individual patient’s risk for vertebral fractures.
XGEVA® can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Based on findings in animals, XGEVA® is expected to result in adverse reproductive effects.
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during therapy, and for at least 5 months after the last dose of XGEVA®. Apprise the patient of the potential hazard to a fetus if XGEVA® is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while patients are exposed to XGEVA®.
The most common adverse reactions in patients receiving XGEVA® with bone metastasis from solid tumors were fatigue/asthenia, hypophosphatemia, and nausea. The most common serious adverse reaction was dyspnea. The most common adverse reactions resulting in discontinuation were osteonecrosis and hypocalcemia.
For multiple myeloma patients receiving XGEVA®, the most common adverse reactions were diarrhea, nausea, anemia, back pain, thrombocytopenia, peripheral edema, hypocalcemia, upper respiratory tract infection, rash, and headache. The most common serious adverse reaction was pneumonia. The most common adverse reaction resulting in discontinuation of XGEVA® was osteonecrosis of the jaw.
XGEVA® is indicated for the prevention of skeletal-related events in patients with multiple myeloma and in patients with bone metastases from solid tumors.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Pre-existing hypocalcemia must be corrected prior to initiating therapy with XGEVA®. XGEVA® can cause severe symptomatic hypocalcemia, and fatal cases have been reported. Monitor calcium levels, especially in the first weeks of initiating therapy, and administer calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D as necessary. Concomitant use of calcimimetics and other drugs that can lower calcium levels may worsen hypocalcemia risk and serum calcium should be..